Variable expenses can be compared year over year to establish a trend and show how profits are affected. The contribution margin formula is calculated by subtracting total variable costs from net sales revenue. The contribution margin is a measurement through which we understand how much a company’s net sales will contribute to the fixed expenses and the net profit after covering the variable expenses. So, we deduct the total variable expenses from the net sales while calculating the contribution. The contribution margin is different from the gross profit margin, the difference between sales revenue and the cost of goods sold. While contribution margins only count the variable costs, the gross profit margin includes all of the costs that a company incurs in order to make sales.
Why You Can Trust Finance Strategists
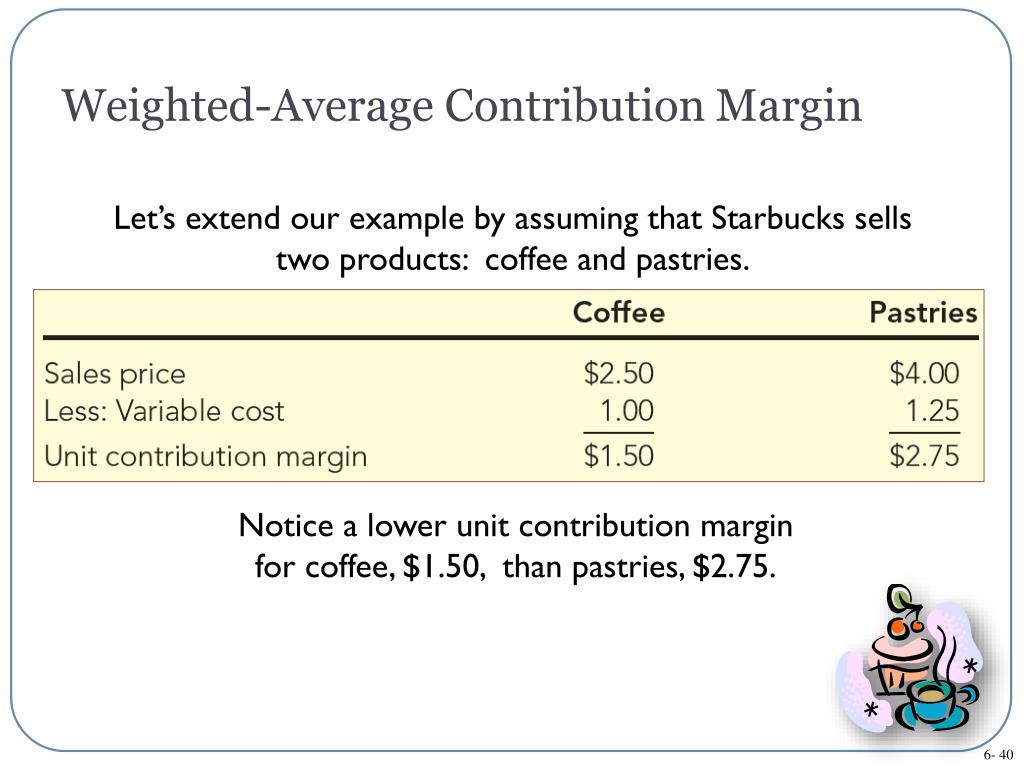
Overall, the unit contribution margin provides valuable insights into the financial performance of individual products or units and helps guide strategic decision-making within organizations. The higher the percentage, the more of each sales dollar is available to pay fixed costs. To determine if the percentage is satisfactory, management would compare the result to previous periods, forecasted performance, contribution margin ratios of similar companies, or industry standards. If the company’s contribution margin ratio is higher than the basis for comparison, the result is favorable. Using this metric, the company can interpret how one specific product or service affects the profit margin. The fixed cost like rent of the premises, salary, wages of laborers, etc will remain the same irrespective of changes in production.
- Recall that Building Blocks of Managerial Accounting explained the characteristics of fixed and variable costs and introduced the basics of cost behavior.
- The contribution margin may also be expressed as fixed costs plus the amount of profit.
- The higher the number, the better a company is at covering its overhead costs with money on hand.
- We explain its formula, differences with gross margin, calculator, along with example and analysis.
How is contribution margin calculated?
Fixed costs are costs that are incurred independent of how much is sold or produced. Buying items such as machinery is a typical example of a fixed cost, specifically a one-time fixed cost. Regardless of how much it is used and how many units are sold, its cost remains the same. However, these fixed costs become a smaller percentage of each unit’s cost as the number of units sold increases.
Contribution Margin Formula
The higher the number, the better a company is at covering its overhead costs with money on hand. Investors examine contribution margins to determine if a company is using its revenue effectively. A high contribution margin indicates that a company tends to bring in more money than it three golden rules of accounting examples pdf quiz more . spends. Fixed costs are often considered sunk costs that once spent cannot be recovered. These cost components should not be considered while making decisions about cost analysis or profitability measures. Another common example of a fixed cost is the rent paid for a business space.
Using this contribution margin format makes it easy to see the impact of changing sales volume on operating income. Fixed costs remained unchanged; however, as more units are produced and sold, more of the per-unit sales price is available to contribute to the company’s net income. The contribution margin represents how much revenue remains after all variable costs have been paid. It is the amount of income available for contributing to fixed costs and profit and is the foundation of a company’s break-even analysis. Here, the variable costs per unit refer to all those costs incurred by the company while producing the product. These include variable manufacturing, selling, and general and administrative costs as well—for example, raw materials, labor & electricity bills.
How to calculate the contribution margin and the contribution margin ratio?

A store owner will pay a fixed monthly cost for the store space regardless of how many goods are sold. Let us understand the step-by-step process of how to calculate using a unit contribution margin calculator through the points below. Next, the CM ratio can be calculated by dividing the amount from the prior step by the price per unit. The greater the contribution margin (CM) of each product, the more profitable the company is going to be, with more cash available to meet other expenses — all else being equal. It’s important to be aware of these limitations when using contribution margin in business decision-making.
This means that the production of grapple grommets produce enough revenue to cover the fixed costs and still leave Casey with a profit of $45,000 at the end of the year. In May, 750 of the Blue Jay models were sold as shown on the contribution margin income statement. When comparing the two statements, take note of what changed and what remained the same from April to May. For example, assume that the students are going to lease vans from their university’s motor pool to drive to their conference. A university van will hold eight passengers, at a cost of $200 per van.
Profit margin is calculated using all expenses that directly go into producing the product. The concept of contribution margin is applicable at various levels of manufacturing, business segments, and products. The contribution margin shows how much additional revenue is generated by making each additional unit of a product after the company has reached the breakeven point. In other words, it measures how much money each additional sale “contributes” to the company’s total profits. Let’s say we have a company that produces 100,000 units of a product, sells them at $12 per unit, and has a variable costs of $8 per unit.
In particular, the use-case of the contribution margin is most practical for companies in setting prices on their products and services appropriately to optimize their revenue growth and profitability potential. While there are plenty of profitability metrics—ranging from the gross margin down to the net profit margin—the contribution margin metric stands out for the analysis of a specific product or service. Therefore, the contribution margin reflects how much revenue exceeds the coinciding variable costs. This is the net amount that the company expects to receive from its total sales. Some income statements report net sales as the only sales figure, while others actually report total sales and make deductions for returns and allowances.
Regardless of how contribution margin is expressed, it provides critical information for managers. Understanding how each product, good, or service contributes to the organization’s profitability allows managers to make decisions such as which product lines they should expand or which might be discontinued. When allocating scarce resources, the contribution margin will help them focus on those products or services with the highest margin, thereby maximizing profits. Contribution per unit is the residual profit left on the sale of one unit, after all variable expenses have been subtracted from the related revenue. This information is useful for determining the minimum possible price at which to sell a product. In essence, never go below a contribution per unit of zero; you would otherwise lose money with every sale.
With that all being said, it is quite obvious why it is worth learning the contribution margin formula. Get instant access to video lessons taught by experienced investment bankers. Learn financial statement modeling, DCF, M&A, LBO, Comps and Excel shortcuts.






